Management of cardiogenic shock associated with valvular heart disease (VHD).
Triggers of Cardiogenic Shock
- Acute events:
- Acute myocardial infarction
- Hypertensive crisis
- Endocarditis
- Pre-existing stable VHD:
- Native aortic stenosis
- Native mitral stenosis
- Structural bio-prosthetic valve degeneration
- Acute onset of severe VHD:
- Primary mitral regurgitation (e.g., chordal rupture, papillary muscle rupture)
- Ischemic mitral regurgitation
- Aortic regurgitation (e.g., Type A aortic dissection)
- Structural bio-prosthetic valve degeneration (e.g., leaflet tear, valve thrombosis)
Initial Management:
- “Check for Futility” Phase:
- Manage triggers (e.g., blood transfusion, electrical cardioversion)
- Administer inotropes and/or vasopressors
- Perform ancillary procedures (e.g., PCI, anticoagulation, fibrinolysis for valve thrombosis)
- Support organ function (e.g., mechanical ventilation, renal replacement therapy)
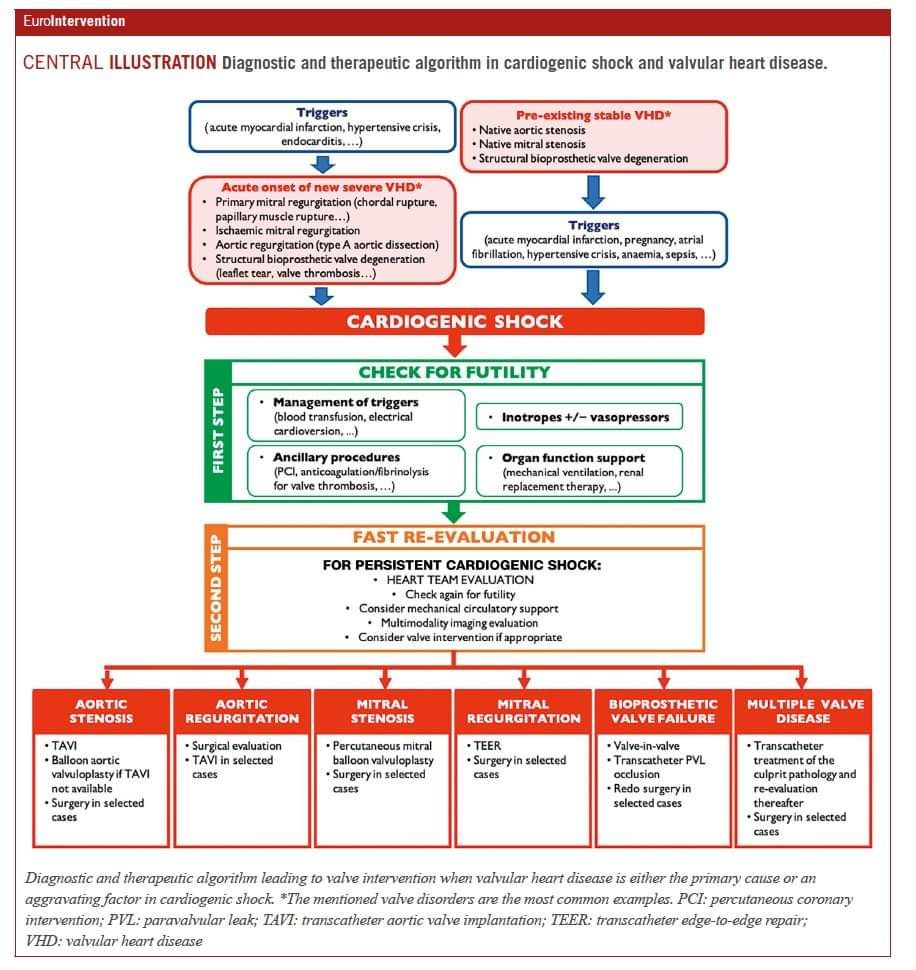
Fast Re-Evaluation for Persistent Cardiogenic Shock:
- Conduct a heart team evaluation.
- Check for futility again.
- Consider:
- Mechanical circulatory support
- Multimodality imaging
- Valve intervention as appropriate.
Valve-Specific Interventions:
Based on the type of VHD:
- Aortic Stenosis:
- TAVI, balloon aortic valvuloplasty, or surgery.
- Aortic Regurgitation:
- Surgical evaluation, TAVI in selected cases.
- Mitral Stenosis:
- Percutaneous mitral balloon valvuloplasty or surgery in selected cases.
- Mitral Regurgitation:
- Transcatheter edge-to-edge repair (TEER) or surgery.
- Bio-prosthetic Valve Failure:
- Valve-in-valve procedures, transcatheter PVL occlusion, or redo surgery.
- Multiple Valve Disease:
- Transcatheter or surgical approaches tailored to the pathology.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.